Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-30 Origin: Site








Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) is one of the most widely used materials in the world, especially in industrial coatings. Its remarkable opacity, UV resistance, and durability make it ideal for a range of applications. However, as demand grows, so does concern about its environmental impact.
In this article, we will explore the environmental consequences of using TiO₂ in coatings. From its production to its disposal, we'll discuss how this material affects air, water, and soil. You’ll also discover solutions for a more sustainable approach to using Titanium Dioxide in coatings.
Titanium Dioxide is a white, naturally occurring mineral that is most commonly used as a pigment in paints and coatings. It’s renowned for its high refractive index, which provides excellent brightness and opacity to coatings. TiO₂ is a key ingredient in products like wall paints, automotive coatings, and protective coatings for industrial materials. Its ability to scatter light makes it essential for applications requiring UV protection and enhanced weather resistance.
Titanium Dioxide is used in two main forms in coatings: rutile and anatase. The rutile form is more stable and is primarily used for its superior opacity and durability. The anatase form is often used in specialized applications, such as photocatalytic coatings that help break down air pollutants under UV light. Both forms are crucial in enhancing the performance and longevity of coatings across industries.
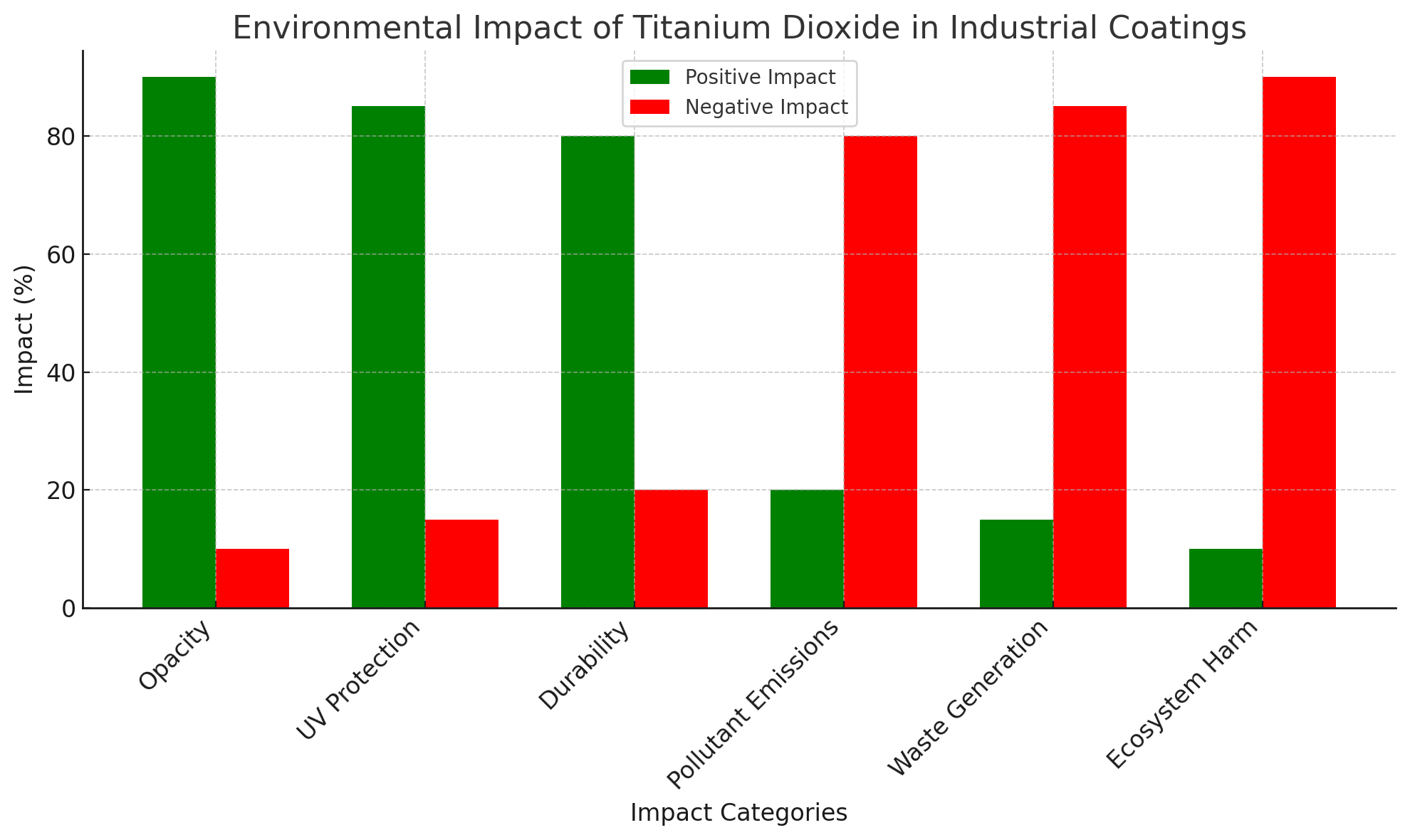
The benefits of Titanium Dioxide in industrial coatings are vast. One of the most notable is its ability to provide high opacity, meaning it can effectively cover surfaces with fewer coats of paint. This reduces material usage and helps lower production costs. TiO₂’s exceptional UV resistance is another significant advantage, especially in outdoor coatings. It helps protect surfaces from sun damage, fading, and degradation, thereby extending the life of the coating and the materials beneath it.
In addition to UV resistance, TiO₂ also offers excellent weather resistance. This makes it ideal for coatings used in harsh environmental conditions, such as coastal regions, where salt and moisture can quickly deteriorate unprotected surfaces. Its stability, coupled with these advantages, makes Titanium Dioxide an indispensable ingredient in many industrial coating formulations.
The production of Titanium Dioxide is not without its environmental costs. The manufacturing process, whether through the sulfate or chloride method, results in the emission of several pollutants. Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are commonly released into the air during TiO₂ production, both of which contribute to acid rain. Acid rain can have devastating effects on ecosystems, particularly on forests, aquatic systems, and soils.
The sulfate process, in particular, is notorious for producing large quantities of sulfuric acid and acidic by-products, which require careful management to avoid soil and water contamination. The chloride process, while somewhat cleaner in terms of emissions, requires high-purity raw materials and strict controls to minimize its environmental impact. Despite these improvements, the overall environmental toll of TiO₂ production remains significant.
Another environmental challenge associated with Titanium Dioxide production is the generation of waste. The manufacturing process produces both solid and liquid waste, often containing heavy metals, acids, and other toxic by-products. These waste products can lead to significant environmental damage if not properly managed.
Solid waste, such as waste sludge, can contaminate soil, causing habitat destruction and long-term ecological consequences. Liquid waste, often containing acidic compounds and heavy metals, can leach into water supplies, harming aquatic life and disrupting local ecosystems. Proper waste management and recycling technologies are crucial in minimizing the environmental impact of TiO₂ production.
The mining of titanium ores, particularly ilmenite, which is the primary source of Titanium Dioxide, also has significant environmental impacts. Titanium ore mining is energy-intensive and often results in the destruction of large areas of land. Mining operations can lead to soil erosion, habitat destruction, and deforestation, particularly in ecologically sensitive areas.
In addition to habitat destruction, mining operations can contribute to water pollution due to the chemicals used in ore extraction. These chemicals can seep into local waterways, affecting water quality and harming aquatic organisms. As demand for titanium dioxide grows, the pressure on mining operations to meet this demand will likely increase, intensifying these environmental impacts unless sustainable practices are adopted.
One of the most pressing environmental concerns related to Titanium Dioxide in coatings is its potential runoff into water systems. TiO₂ particles, especially in nanoparticle form, are small enough to be washed away by rain or runoff during the application and aging of coatings. Once in water systems, these nanoparticles can have a detrimental effect on aquatic life.
Studies have shown that TiO₂ nanoparticles can accumulate in aquatic organisms, disrupting nutrient cycles and harming ecosystems. These particles may interfere with the growth and reproduction of algae and other aquatic plants, which are essential to the food chain. Furthermore, TiO₂ particles can alter the pH of water bodies, making them more acidic and harmful to marine life.
The application of TiO₂ coatings, particularly in spray form, can result in the release of TiO₂ particles into the air. These airborne particles, while not typically harmful in low concentrations, can contribute to air pollution when inhaled in larger amounts. In occupational settings, workers applying coatings may be at risk of respiratory issues due to prolonged exposure to TiO₂ aerosols.
While TiO₂ itself is non-toxic in its solid form, the fine particles in industrial coatings can contribute to dust accumulation in the air, affecting both air quality and worker health. Long-term exposure to these particles can lead to respiratory issues such as asthma or other pulmonary diseases. Adequate ventilation and protective measures, such as masks and respirators, are necessary to minimize exposure in industrial environments.
In addition to water and air pollution, Titanium Dioxide coatings can contribute to soil contamination. The accumulation of TiO₂ particles in soil can occur over time, especially in areas where coatings are applied to outdoor surfaces. Once in the soil, TiO₂ particles can affect plant growth and soil fertility.
Because TiO₂ is chemically inert and non-biodegradable, it does not break down naturally over time. As a result, these particles can persist in the soil for extended periods, potentially disrupting ecosystems and reducing the natural biodiversity of the area. The long-term effects of this soil contamination are still under study, but the potential for ecological harm remains a concern.
Nano-Titanium Dioxide has become increasingly popular in coatings due to its unique properties. Nano-sized particles have a high surface area to volume ratio, which enhances their ability to disperse in coatings and provide superior opacity and UV protection. Nano-TiO₂ is particularly effective in self-cleaning and photocatalytic coatings, where it helps break down organic pollutants when exposed to UV light.
Despite its advantages, the use of nano-TiO₂ in coatings raises several environmental and health concerns. Due to its small size, nano-TiO₂ particles can easily penetrate biological barriers, such as cell membranes, and may accumulate in the environment, leading to long-term ecological consequences.
One of the main concerns surrounding nano-TiO₂ is its potential toxicity. Due to its extremely small size, nano-TiO₂ particles can penetrate cell membranes and tissues more easily than larger particles. Prolonged exposure to these nanoparticles could result in inflammation, cell damage, and other toxicological effects.
In aquatic environments, nano-TiO₂ particles can be ingested by marine organisms, leading to bioaccumulation. This means that the particles could enter the food chain, potentially harming higher organisms, including fish and humans. While research is still ongoing, the potential for environmental and health risks from nano-TiO₂ exposure is a growing concern for industries using this material in coatings.
Currently, there is a lack of comprehensive regulations governing the use of nano-TiO₂ in industrial coatings. Nano-TiO₂ particles are often treated the same as bulk TiO₂, despite their significantly different properties and potential environmental impact. As the use of nano-TiO₂ increases, regulatory bodies must update safety standards to address the unique risks posed by these particles.
The lack of clear guidelines and safety standards for nano-TiO₂ in coatings is a significant challenge. More research is needed to better understand the long-term environmental and health impacts of nano-TiO₂ particles. This knowledge will help inform the development of safer and more sustainable products.
The production of Titanium Dioxide can be made more sustainable through the adoption of cleaner production technologies. Innovations in the sulfate and chloride production processes are reducing emissions and minimizing waste. For example, new methods for capturing and recycling sulfuric acid from the production process can help reduce the environmental impact of TiO₂ manufacturing.
Additionally, advancements in energy-efficient technologies, such as the use of renewable energy sources in TiO₂ production, are helping to decrease the carbon footprint of the industry. By investing in these cleaner technologies, manufacturers can reduce the overall environmental impact of TiO₂ production.
Recycling TiO₂ from used coatings can significantly reduce the need for new raw materials and help minimize waste. Several technologies are now being developed to recover TiO₂ from industrial scrap and used coatings, which can then be reprocessed and reused in new formulations. This not only reduces the environmental impact of TiO₂ production but also lowers costs for manufacturers.
Encouraging the recycling of TiO₂-based products is a key step in creating a circular economy. By reusing TiO₂ in coatings, industries can reduce the demand for new materials, conserve resources, and minimize waste. As recycling technologies continue to improve, TiO₂ reuse will play an increasingly important role in the sustainability of the coatings industry.
Reducing the amount of TiO₂ used in coatings without compromising performance is another way to mitigate the environmental impact of industrial coatings. Innovations in coating formulations are allowing manufacturers to use less TiO₂ while maintaining opacity, durability, and UV protection. This not only helps conserve resources but also reduces the overall environmental footprint of TiO₂ production.
By focusing on high-dispersion TiO₂ and using advanced pigment technologies, manufacturers can achieve the same performance with a smaller amount of TiO₂. This reduction in TiO₂ content can have a significant positive impact on the environment by lowering the demand for raw materials and reducing waste.
The global regulatory landscape for Titanium Dioxide is evolving as more is learned about its environmental and health impacts. In the European Union, TiO₂ has been banned as a food additive due to concerns about its potential carcinogenicity when inhaled in its nanoparticle form. However, in other regions, such as the United States, TiO₂ continues to be widely used in food products, cosmetics, and coatings.
The differences in regulations between regions highlight the need for more consistent and comprehensive global standards for TiO₂ use. As the industry faces growing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, governments must update regulations to ensure the safe use of TiO₂ and its derivatives in consumer products.
Manufacturers of Titanium Dioxide are increasingly required to comply with environmental standards aimed at reducing pollution and promoting sustainability. Compliance with these regulations involves adopting cleaner production processes, minimizing waste, and ensuring the safe disposal of by-products. Eco-certifications and sustainability labels are becoming more important, helping consumers make informed choices about the products they purchase.
As the industry shifts toward greater environmental responsibility, it is essential for manufacturers to remain compliant with evolving regulations. This will not only help mitigate the environmental impact of TiO₂ but also enhance the sustainability of industrial coatings.
Looking ahead, the future of Titanium Dioxide in industrial coatings will be shaped by trends in sustainability and technological innovation. As demand for greener alternatives grows, manufacturers will continue to explore new ways to reduce the environmental impact of TiO₂. This includes the development of new production processes that minimize waste and energy consumption, as well as the creation of more efficient and environmentally-friendly TiO₂-based products.
The adoption of sustainable practices, such as recycling TiO₂ and reducing its use in coatings, will be critical in meeting both environmental goals and industry demands. By embracing these innovations, the coatings industry can continue to thrive while minimizing its ecological footprint.
Titanium Dioxide plays a key role in industrial coatings, providing excellent opacity, UV protection, and durability. However, its production, use, and disposal raise environmental concerns, including pollutant emissions, waste, and ecosystem damage. By adopting cleaner manufacturing practices and improving recycling, the industry can reduce these impacts.
As sustainability becomes a priority, companies like Huilong Baichuan offer high-quality, environmentally responsible TiO₂ solutions. These products help balance performance with eco-friendly practices, ensuring long-term benefits for industries worldwide.
A: Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) is a white pigment widely used in industrial coatings for its excellent opacity, UV resistance, and durability, making it ideal for paints and coatings.
A: The production of Titanium Dioxide releases pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, contributing to air pollution and acid rain. Additionally, mining practices can cause habitat destruction and deforestation.
A: Yes, TiO₂ nanoparticles in coatings can leach into water and soil, potentially harming aquatic life and disrupting ecosystems.
A: Cleaner production technologies, recycling of TiO₂ from used coatings, and reducing its content in formulations can help mitigate environmental impacts.
A: TiO₂ offers unparalleled opacity, UV protection, and durability, making it essential for high-performance coatings, even though it poses environmental challenges during production and disposal.